pmKate2-mito is a mammalian expression vector intended for far-red fluorescent labeling of mitochondria in living cells. The vector encodes far-red fluorescent protein mKate2 (see reporter description) fused to mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) derived from the subunit VIII of human cytochrome C oxidase [Rizzuto et al., 1989; Rizzuto et al., 1995]. MTS is fused to the mKate2 N-terminus.
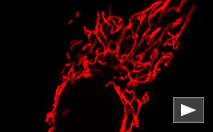
 | Laser scanning confocal imaging of mKate2 fused to a mitochondrial targeting signal peptide expressed in fox lung fibroblast cells. |
mKate2 codon usage is optimized for high expression in mammalian cells (humanized) [Haas et al., 1996].
pmKate2-mito vector can be used as a source of mKate2-MTS hybrid sequence. The vector backbone contains unique restriction sites that permit its excision and further insertion into expression vector of choice.
Note: The plasmid DNA was isolated from dam+-methylated
The vector backbone contains immediate early promoter of cytomegalovirus (PCMV IE) for protein expression, SV40 origin for replication in mammalian cells expressing SV40 T-antigen, pUC origin of replication for propagation in
SV40 early promoter (PSV40) provides neomycin resistance gene (Neor) expression to select stably transfected eukaryotic cells using G418. Bacterial promoter (P) provides kanamycin resistance gene expression (Kanr) in
Expression in mammalian cells
pmKate2-mito vector can be transfected into mammalian cells by any known transfection method. CMV promoter provides strong, constitutive expression of the mKate2-MTS fusion in eukaryotic cells. If required, stable transformants can be selected using G418 [Gorman, 1985].
Propagation in
Suitable host strains for propagation in